Language and Index Control
Special Word Stems
This section allows managing words where automatic stemming (reducing a word to its root form) causes undesirable effects. This applies particularly to:
- Irregular plurals
- Foreign words
- Brand names
Here, it is possible to:
- Define the correct word stem.
- Prevent a word from being stemmed at all.
Examples
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
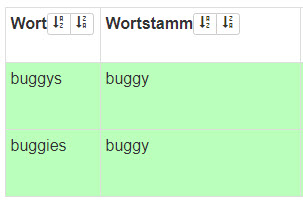 | Searching for “Buggys” automatically stems it to “Buggy”. |
 | Searching for “Slipper” remains unchanged. Without this setting, the algorithm would stem it to “Slip”, which has a completely different meaning. |
 | Searching for “Balloon” remains unchanged. Without this setting, the algorithm would stem it to “Ball”, which is incorrect. |
Data Management – Stop Words
Stop words are words (typically filler words) that should be ignored in search queries because they do not help in finding the most relevant products.
These words are:
- Removed from search input before processing.
- Not included in the search index.
Example Stop Words
- “also”
- “again”
- “the”
Data Management – Word List
The word list functions as a dictionary for the respective language.
In German, this is particularly important for correctly splitting compound words during searches.
Purpose of the Word List
- Ensures proper word segmentation in search queries.
- Helps recognize compound words in German.
- Allows foreign words to be added when necessary for correct processing.
Maintenance
- The word list rarely requires updates.
- Occasionally, foreign words need to be added to ensure correct word splitting.
Data Management – SEO Filter List
This function allows generating and exporting a complete list of filters, including their corresponding filter values and URL parameters.
Functionality and Contents
- The filter list generation starts automatically when accessing the menu.
- If successful, a confirmation message appears.
- The list can be downloaded via the “Download Filter List” button.
Export File Format
- The filter list is exported as a TXT file.
- It contains all available filters and filter values.
- The file includes the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Filter Name | Internal identifier (ID) of the filter. |
| Filter Label | Name of the filter as displayed in the shop. |
| Filter Value | Technical name of the filter value. |
| Filter Value Label | Name of the filter value as displayed in the shop. |
| URL Parameter | The URL parameter for the filter and value. Appending this parameter to a URL applies the filter directly. |
Data Management – Excluding Categories from the Search Index
This function allows defining categories whose names should not be included in the search index for associated products.
This is useful for broad categories that contain multiple product types, such as “Jewelry & Watches”, which can lead to irrelevant search results.
Why Exclude Categories?
If category names are indexed, irrelevant results may appear.
Example Issue
- A user searches for “watches men”.
- The search looks for both words in all indexed categories.
- A “Necklace for Men” in the “Jewelry & Watches” category is found.
- However, a necklace is not a men’s watch, making the result incorrect.
Additionally, category names become a high-value field in the search index. They can be configured with no or only a small penalty during ranking.
Configuration
Adding a Category to the Exclusion List
-
Click “Add New Excluded Category”. The category tree opens in a modal.
-
Choose a category using one of two methods:
- Manual navigation through the tree
- Search (e.g., searching for “watches” highlights relevant nodes in red)
-
Select a category and click “Add”. Selections must be added individually.